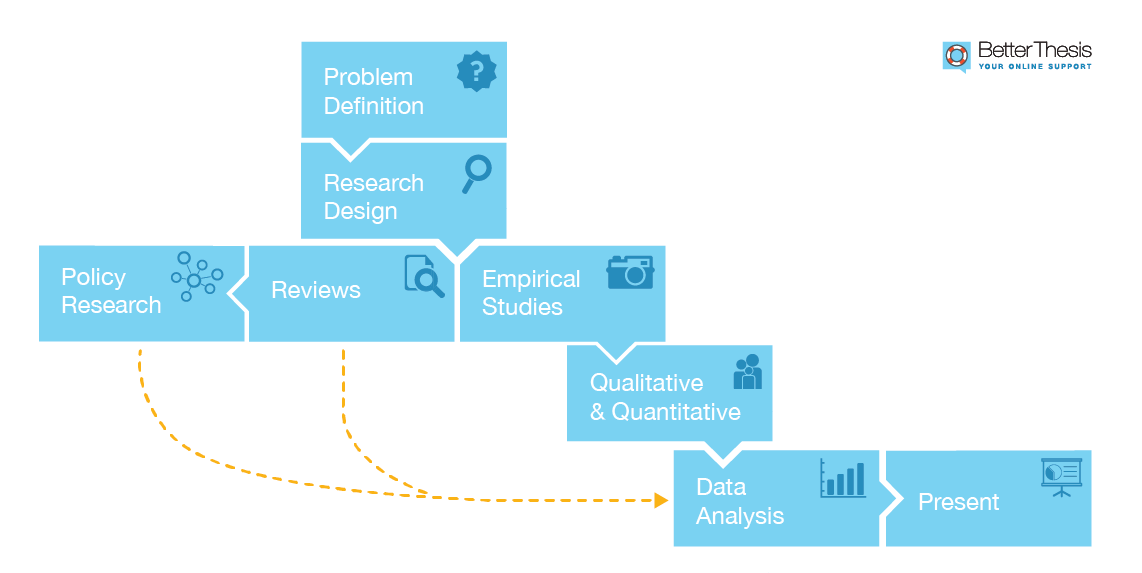
Research Methods: Summary
Research methods are generalised and established ways of approaching research questions. Research methods are divided into qualitative and quantitative approaches and involve the specific study activities of collecting and analyzing research data in order to answer the particular research question.
Not all methods can be applied to all research questions:
- Qualitative methods should be deployed when the research aim is an in-depth, contextual analysis of a phenomenon. These methods are very good for answering the what and who questions, but not well suited to answering why and where research questions.
- Quantitative methods should be deployed when the research aim is to produce generalizable results that show prevalence, incidence, statistical relationships between variables and causation. These methods are well suited to answering why and where questions, but may lack a deep understanding of a phenomenon, particularly if the research area is of a sensitive nature.
Data collection methods can be used in various study types, including:
- Empirical studies – These are field based studies during which the research collects primary data.
- Desk Reviews – These are non-filed based studies during which the researcher analyses and synthesises secondary data to articulate new findings.
- Research Analysis and Evalaution – These can be either field studies or desk reviews during which the researcher aims to recommend the best policy or program option before implementation or aims to articulate the impact of a policy or program after implementation.